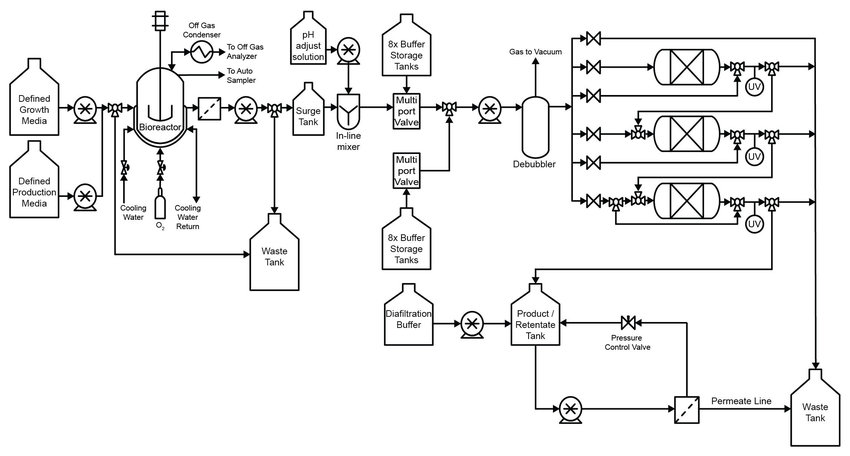
Best Practices for P&ID Development

Excavation and Trenching Safety Training: A Comprehensive Guide by The Safety Master
December 30, 2024
Understanding Electrical Hazards
December 31, 2024Piping and Instrumentation Diagrams (P&IDs) are critical components in the design and operation of process facilities. These detailed diagrams provide a graphical representation of the physical sequence of equipment and systems, along with the instrumentation and control devices that manage the processes. Given their importance, it is essential to adhere to best practices in their development to ensure accuracy and consistency. Additionally, understanding the role of P&IDs in process safety and operational efficiency can significantly enhance their utility.
Best Practices for P&ID Development
- Standardization: Utilizing industry standards such as ISA (International Society of Automation) and ISO (International Organization for Standardization) can help in maintaining uniformity across P&IDs. These standards provide guidelines on symbols, terminology, and layout, ensuring that diagrams are easily understood by all stakeholders.
- Detailed Documentation: Every component in the process should be accurately documented in the P&ID. This includes all piping, equipment, instrumentation, and control devices. Clear and detailed documentation helps in avoiding any ambiguities during the construction and operation phases.
- Consistent Use of Symbols: Consistency in the use of symbols is crucial. Different teams working on the project should use the same symbols to represent the same types of equipment and instruments. This helps in reducing confusion and errors.
- Regular Reviews and Updates: P&IDs should be regularly reviewed and updated to reflect any changes in the process. This ensures that the diagrams remain accurate and reliable sources of information.
- Integration with Other Documentation: P&IDs should be integrated with other key documents such as process flow diagrams (PFDs), control narratives, and safety documentation. This integration ensures a holistic view of the process and aids in better decision-making.
- Training and Competency: Ensuring that all personnel involved in the development and use of P&IDs are adequately trained and competent is essential. Regular training programs and competency assessments can help in maintaining high standards.
- Use of Software Tools: Leveraging advanced software tools can enhance the accuracy and efficiency of P&ID development. These tools offer features such as automated symbol libraries, error checking, and easy updates.
Role of P&IDs in Process Safety
- Hazard Identification and Risk Assessment: P&IDs play a crucial role in hazard identification and risk assessment (HIRA) processes. They provide a detailed view of the process, helping in identifying potential hazards and assessing risks associated with different process stages.
- Operational Control: Accurate P&IDs ensure that all control systems are correctly implemented and functioning as intended. This helps in maintaining operational control and preventing deviations that could lead to safety incidents.
- Emergency Response Planning: P&IDs are vital for emergency response planning. They provide critical information about the process layout and control systems, which can be used to develop effective emergency response strategies.
- Compliance and Auditing: Regulatory bodies often require detailed P&IDs as part of compliance and auditing processes. Accurate and up-to-date P&IDs can help in demonstrating compliance with safety regulations and standards.
Role of P&IDs in Operational Efficiency
- Process Optimization: P&IDs provide a comprehensive view of the process, allowing engineers to identify areas for optimization. This can lead to improved efficiency and reduced operational costs.
- Maintenance Planning: Detailed P&IDs help in effective maintenance planning. They provide information about the location and specifications of equipment, aiding in the development of maintenance schedules and procedures.
- Troubleshooting: In the event of a process upset or failure, P&IDs can be invaluable for troubleshooting. They offer a detailed view of the process and control systems, helping engineers quickly identify and rectify issues.
- Training and Onboarding: P&IDs are essential tools for training and onboarding new personnel. They provide a visual representation of the process, helping new employees understand the system and their roles within it.
In conclusion, P&IDs are indispensable tools in the design, operation, and maintenance of process facilities. Adhering to best practices in their development ensures accuracy and consistency, while understanding their role in process safety and operational efficiency enhances their utility. By following these guidelines, organizations can ensure that their P&IDs are reliable, accurate, and valuable resources for all stakeholders.